Breaking Barriers, Localizing Saliency:
A Large-scale Benchmark and Baseline for Condition-Constrained Salient Object Detection
2 Lingnan University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Abstract
Salient Object Detection (SOD) aims to identify and segment the most prominent objects in an image. In real open environments, intelligent systems often encounter complex and challenging scenes, such as low-light, rain, snow, \etc, which we call constrained conditions. These real situations pose more severe challenges to existing SOD models. However, there is no comprehensive and in-depth exploration of this field at both the data and model levels, and most of them focus on ideal situations or a single condition. To bridge this gap, we launch a new task, Condition-Constrained Salient Object Detection (CSOD), aimed at robustly and accurately locating salient objects in constrained environments. On the one hand, to compensate for the lack of datasets, we construct the first large-scale condition-constrained salient object detection dataset CSOD10K, comprising 10,000 pixel-level annotated images and over 100 categories of salient objects. This dataset is oriented towards the real environment and includes 8 real-world constrained scenes under 3 main constraint types, making it extremely challenging. On the other hand, we abandon the paradigm of "restoration before detection" and instead introduce a unified end-to-end framework CSSAM that fully explores scene attributes, eliminating the need for additional ground-truth restored images and reducing computational overhead. Specifically, we design a Scene Prior-Guided Adapter (SPGA), which injects scene priors to enable the foundation model to better adapt to downstream constrained scenes. To automatically decode salient objects, we propose a Hybrid Prompt Decoding Strategy (HPDS), which can effectively integrate multiple types of prompts to achieve adaptation to the SOD task. Extensive experiments show that our model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on both the CSOD10K dataset and existing standard SOD benchmarks.
CSOD10K Dataset
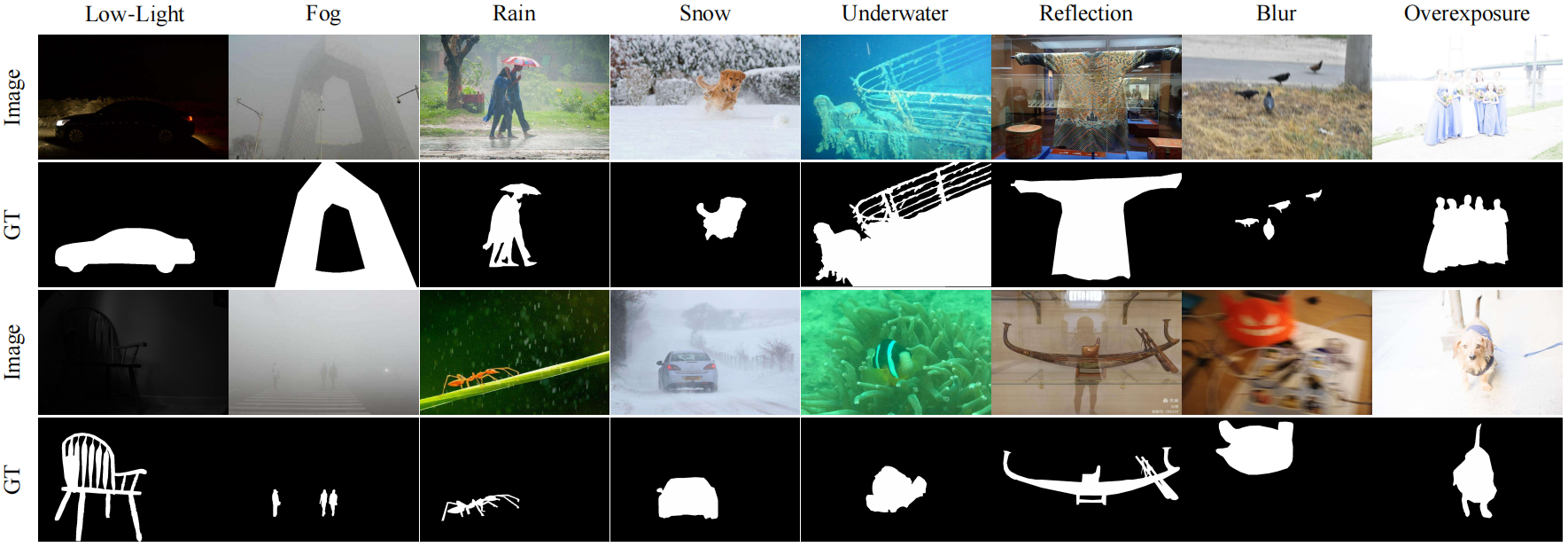

This study introduces the CSOD10K dataset, a new large-scale benchmark explicitly designed for salient object detection in various constrained conditions, which enables us to train and evaluate state-of-the-art SOD methods. The above figure presents some images from the CSOD10K dataset along with their ground truth.
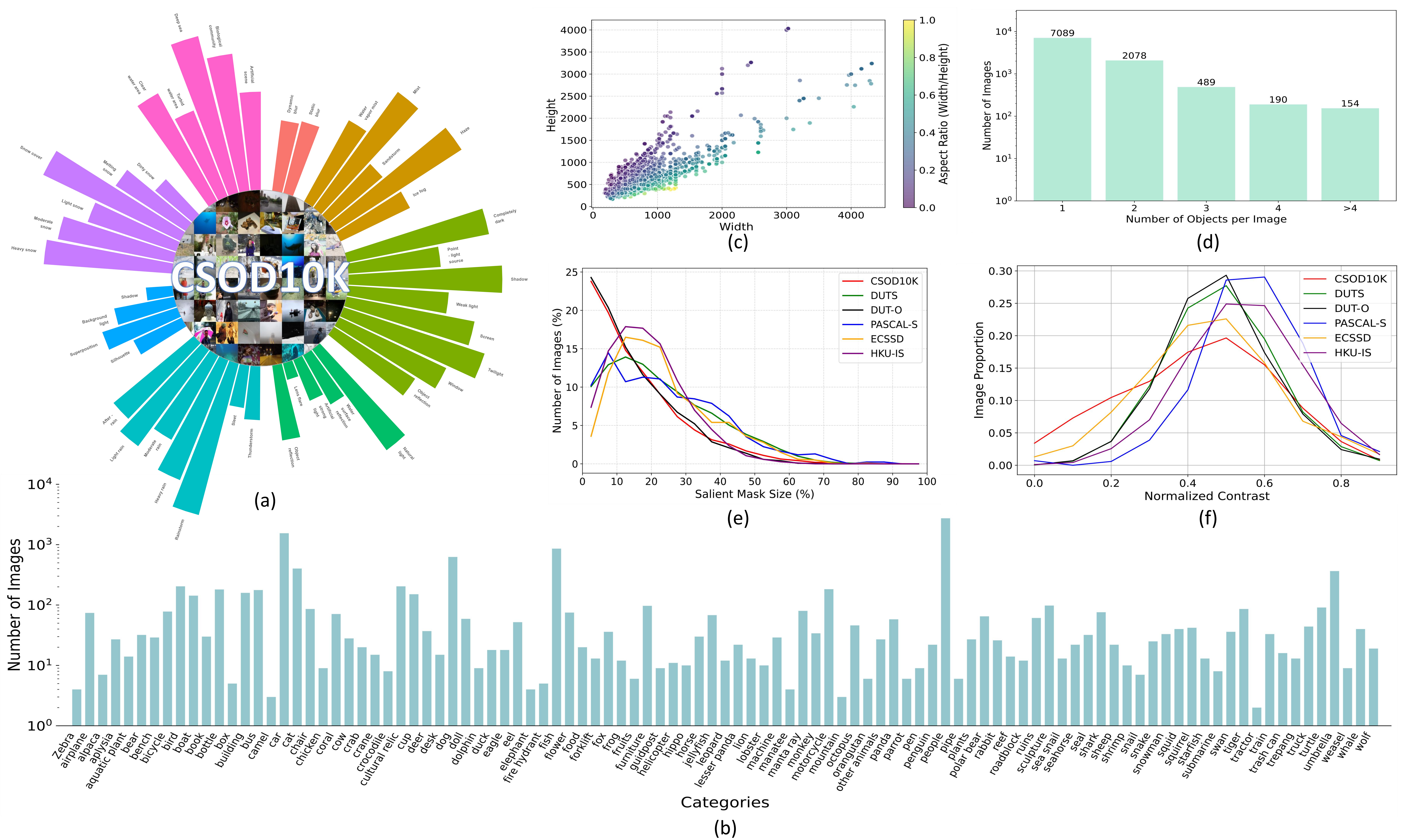
Statistics from the CSOD10K dataset. (a) Fine-grained classification of constrained scenes, where the bar length represents the number of images. (b) Number of images for each salient object category. (c) Image resolution distribution. (d) Distribution of the number of salient objects per image. (e) The comparison of the size of salient objects with other SOD datasets, where the horizontal axis refers to the proportion of salient objects mask to the total number of pixels in the image. (f) Comparison of CSOD10K and other datasets in color contrast.
Pipeline
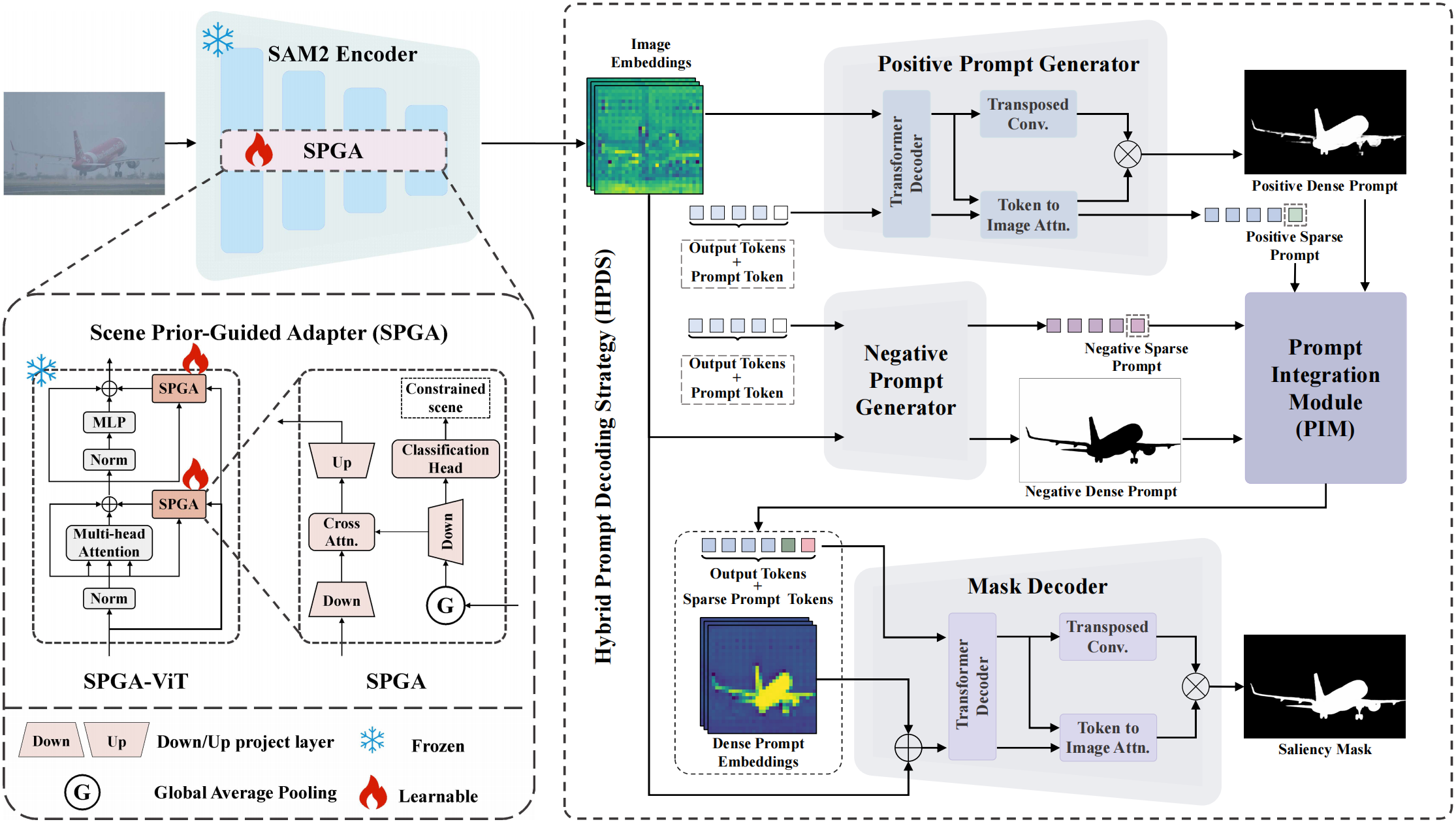
The overall framework of the proposed CSSAM. During the encoding stage, we freeze the parameters of the image encoder and incorporate the Scene Prior-Guided Adapter (SPGA) into the encoder for parameter-efficient fine-tuning to adapt to constrained scenes. In the decoding stage, we use Hybrid Prompt Decoding Strategy (HPDS) to adapt to the SOD task. First, we obtain four types of prompts through the Positive and Negative Prompt Generator. Second, the Prompt Integration Module (PIM) fuses multiple prompts. Finally, the mask decoder outputs the saliency mask.
Highlights
We launch a new task, Condition-Constrained Salient Object Detection (CSOD), and provide solutions from the two dimensions of data and model, enabling intelligent systems to more reliably address complex visual challenges in real and open environments.
We construct a large-scale benchmark dataset CSOD10K for the CSOD task. It is the first SOD dataset covering diverse constrained conditions, with 10,000 images, 3 main constraint types, 8 real-world scenes, 101 object categories, and pixel-level annotations, providing a rich experimental basis and exploration opportunities for the research community.
We propose a unified end-to-end framework CSSAM for the CSOD task. We design a Scene Prior-Guided Adapter (SPGA) to enable the foundation model to better adapt to downstream constrained scenes. We propose a Hybrid Prompt Decoding Strategy (HPDS) that effectively generates and integrates multiple types of prompts to achieve adaptation to the SOD task.
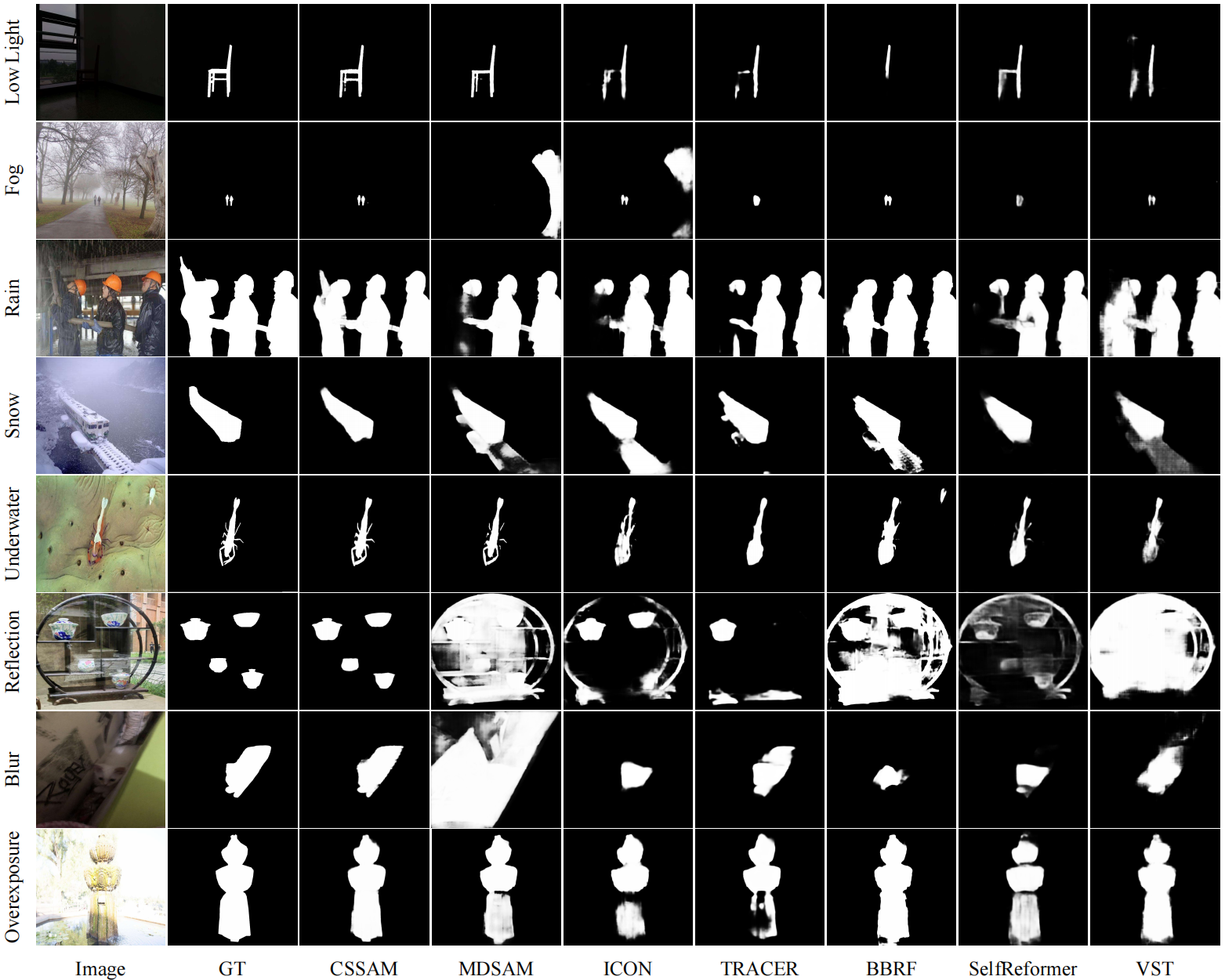
Results
Contact
If you have any questions, please contact Runmin Cong at rmcong@sdu.edu.cn.

