Does Thermal Really Always Matter for RGB-T Salient Object Detection?
2 Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
4 City University of Hong Kong, China
Abstract
In recent years, RGB-T salient object detection (SOD) has attracted continuous attention, which makes it possible to identify salient objects in environments such as low light by introducing thermal image. However, most of the existing RGB-T SOD models focus on how to perform cross-modality feature fusion, ignoring whether thermal image is really always matter in SOD task. Starting from the definition and nature of this task, this paper rethinks the connotation of thermal modality, and proposes a network named TNet to solve the RGB-T SOD task. In this paper, we introduce a global illumination estimation module to predict the global illuminance score of the image, so as to regulate the role played by the two modalities. In addition, considering the role of thermal modality, we set up different cross-modality interaction mechanisms in the encoding phase and the decoding phase. On the one hand, we introduce a semantic constraint provider to enrich the semantics of thermal images in the encoding phase, which makes thermal modality more suitable for the SOD task. On the other hand, we introduce a two-stage localization and complementation module in the decoding phase to transfer object localization cue and internal integrity cue in thermal features to the RGB modality. Extensive experiments on three datasets show that the proposed TNet achieves competitive performance compared with 20 state-of-the-art methods.
Pipeline
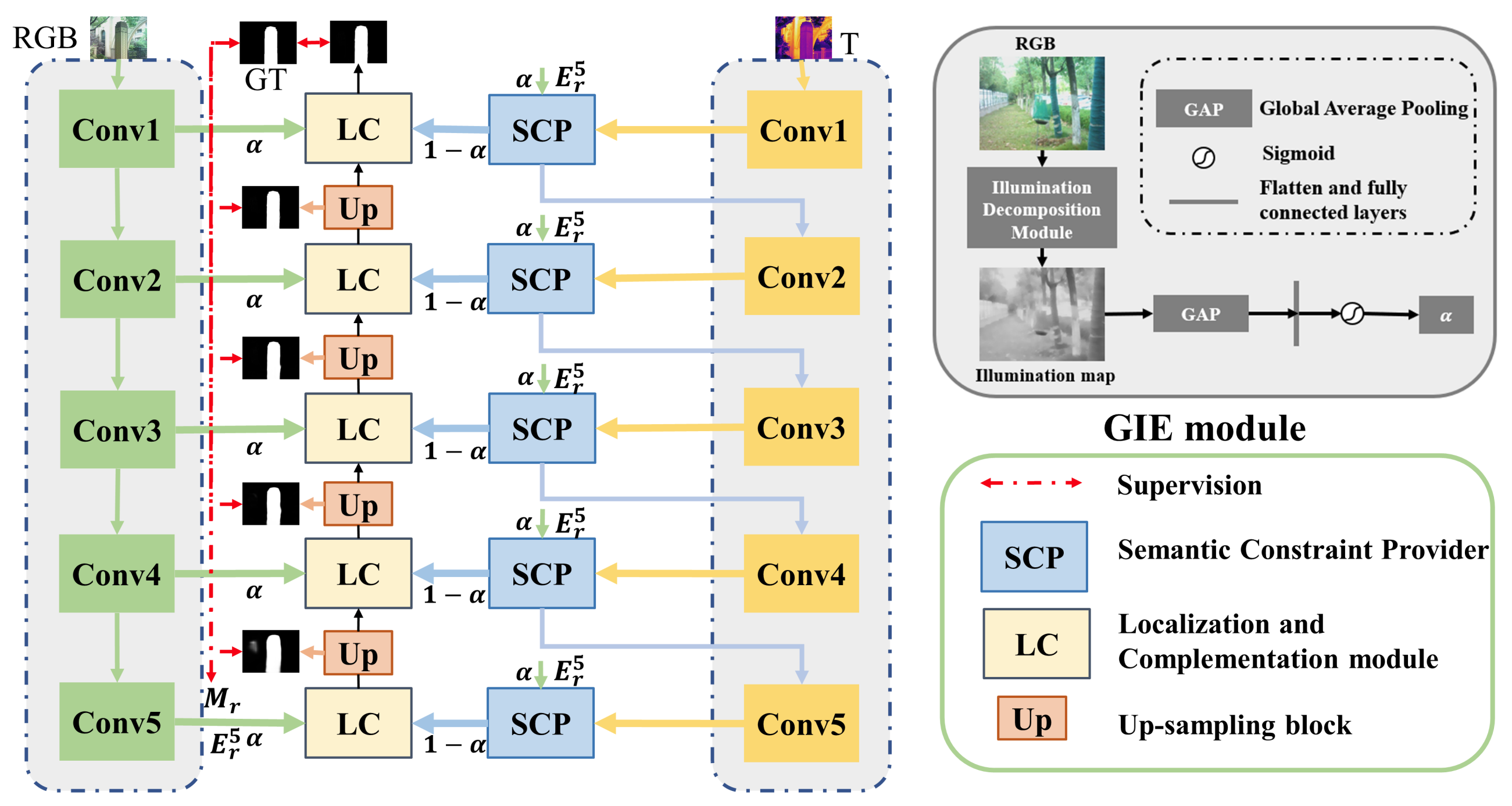
The overview architecture of the proposed TNet, which follows an encoder-decoder structure. The upper right corner is the global illumination estimation (GIE) module, predicting a global illuminance score to control the role of the two modalities. In the dual-stream encoding, the semantic constraint provider (SCP) module is introduced to enrich the thermal features with the help of high-level RGB semantics, making it more suitable for SOD tasks. Finally, the single-stream decoding with the RGB modality as the dominant and the thermal modality as the auxiliary implements layer-by-layer decoding under the action of the localization and complementation (LC) module, thereby obtaining the final saliency prediction.
Highlights
We rethink the value and role of thermal images in SOD task, and propose a global illumination estimation module to control and regulate the interaction between the RGB image and the thermal image, thereby better adapting to challenging scenes such as low light.
In the encoding stage, a semantic constraint provider is designed to supplement the semantic content for each layer of the thermal image branch, which makes the thermal features more suitable for the SOD task.
In the decoding stage, a localization and complementation module is developed, which uses thermal features to provide effective object localization and integrity information for RGB decoding features.
The proposed network achieves superior performance compared to 20 state-of-the-art methods on three public benchmark datasets.
Qualitative Evaluation
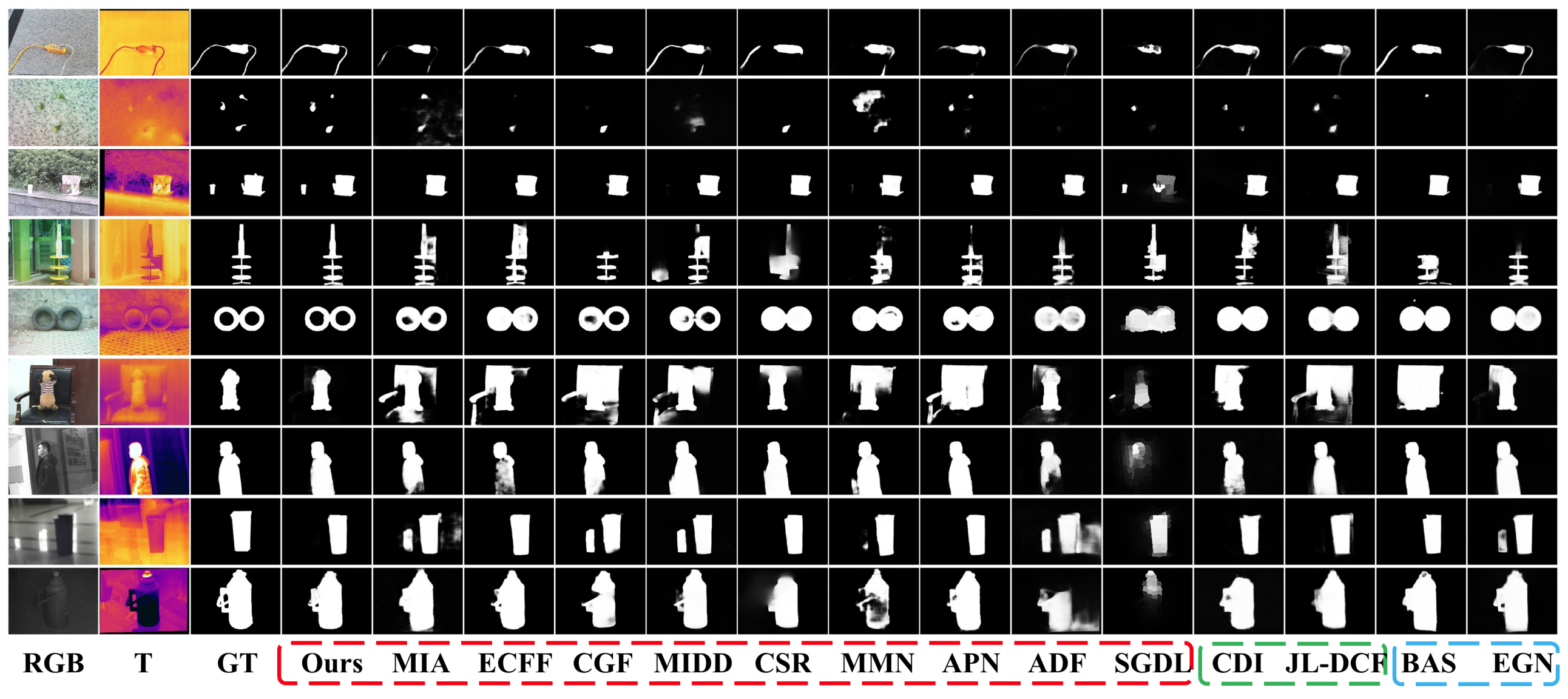
Qualitative visual comparison of different methods, including nine state-of-the-art RGB-T SOD methods marked in red dotted box, two RGB-D SOD methods marked in green dotted box, and two RGB SOD methods marked in blue dotted box.
Quantitative Evaluation
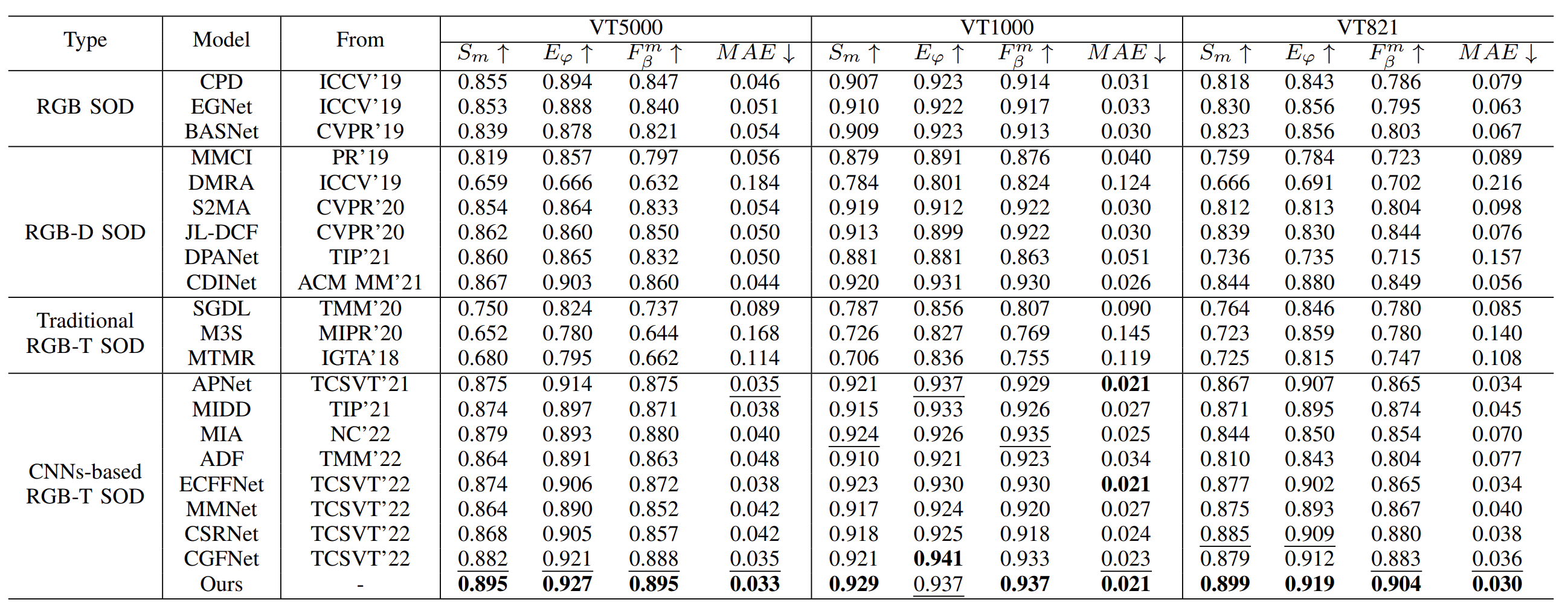
Quantitative comparison results of different models. ↑/↓ for a metric denotes that a larger/smaller value is better. The best results are in bold and the second best results are highlighted in underline.
Citation
@article{TNet,
title={Does Thermal Really Always Matter for {RGB-T} Salient Object Detection?},
author={Cong, Runmin and Zhang, Kepu and Zhang, Chen and Zheng, Feng and Zhao, Yao and Huang, Qingming and Kwong, Sam },
journal={IEEE Transactions on Multimedia},
year={2022},
publisher={IEEE}
}
Contact
If you have any questions, please contact Runmin Cong at rmcong@bjtu.edu.cn.

